[ad_1]

Miragec/Getty Pictures
Google has been caught internet hosting a malicious advert so convincing that there’s a good likelihood it has managed to trick a few of the extra security-savvy customers who encountered it.
Malwarebytes
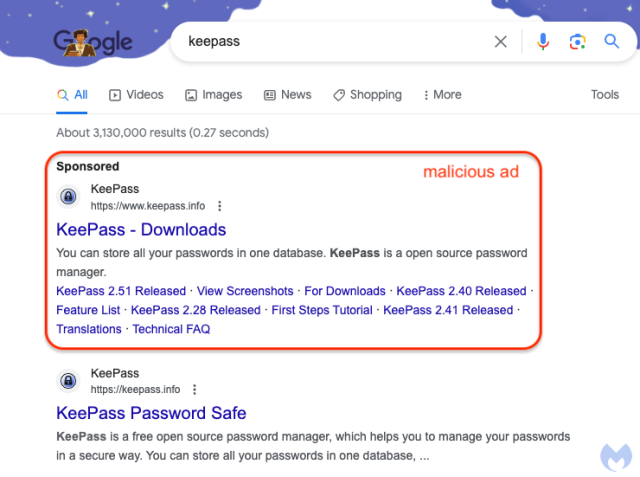
Trying on the advert, which masquerades as a pitch for the open-source password supervisor Keepass, there’s no method to know that it’s pretend. It’s on Google, in spite of everything, which claims to vet the advertisements it carries. Making the ruse all of the extra convincing, clicking on it results in ķeepass[.]information, which when seen in an handle bar seems to be the genuine Keepass site.
Malwarebytes
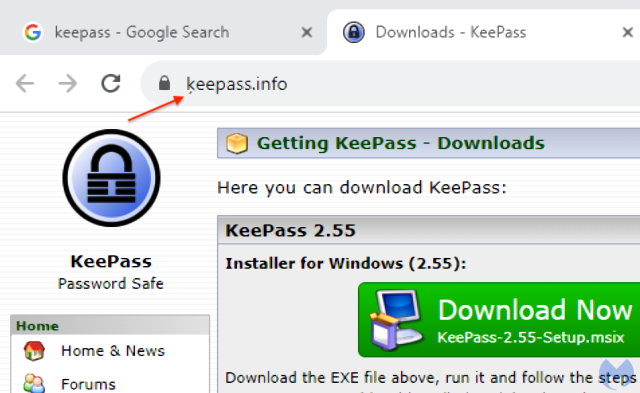
A more in-depth hyperlink on the hyperlink, nevertheless, reveals that the location is not the real one. In actual fact, ķeepass[.]information —not less than when it seems within the handle bar—is simply an encoded approach of denoting xn--eepass-vbb[.]information, which it seems, is pushing a malware household tracked as FakeBat. Combining the advert on Google with an internet site with an nearly equivalent URL creates a close to good storm of deception.
“Customers are first deceived through the Google advert that appears completely legit after which once more through a lookalike area,” Jérôme Segura, head of menace intelligence at safety supplier Malwarebytes, wrote in a post Wednesday that exposed the rip-off.
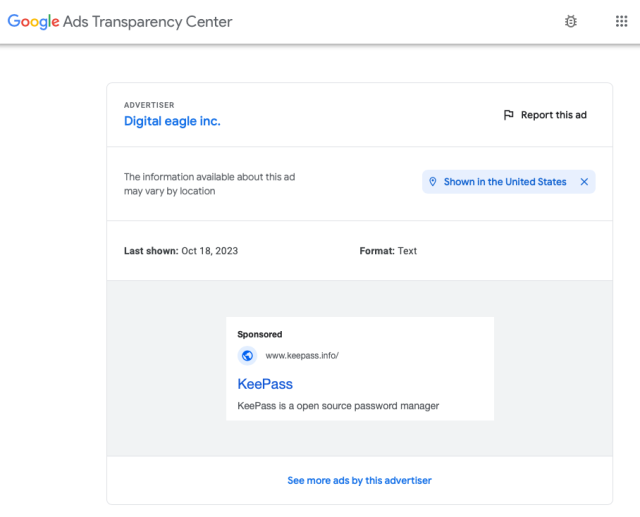
Data obtainable by way of Google’s Advert Transparency Middle reveals that the advertisements have been operating since Saturday and final appeared on Wednesday. The advertisements had been paid for by an outfit known as Digital Eagle, which the transparency web page says is an advertiser whose identification has been verified by Google.
Malwarebytes
Google representatives didn’t instantly reply to an e-mail, which was despatched after hours. Previously, the corporate has stated it promptly removes fraudulent advertisements as quickly as attainable after they’re reported.
The sleight of hand that allowed the imposter website xn--eepass-vbb[.]information to look as ķeepass[.]information is an encoding scheme often known as punycode. It permits unicode characters to be represented in commonplace ASCII textual content. Trying rigorously, it’s simple to identify the small comma-like determine instantly under the okay. When it seems in an handle bar, the determine is equally simple to overlook, particularly when the URL is backed by a legitimate TLS certificates, as is the case right here.
Using punycode-enhanced malware scams has an extended historical past. Two years in the past, scammers used Google advertisements to drive folks to a website that regarded almost identical to courageous.com, however was, in truth, one other malicious web site pushing a pretend, malicious model of the browser. The punycode method first got here to widespread consideration in 2017, when a Net software developer created a proof-of-concept website that masqueraded as apple.com.
There’s no sure-fire method to detect both malicious Google advertisements or punycode encoded URLs. Posting ķeepass[.]information into all 5 main browsers results in the imposter website. When unsure, folks can open a brand new browser tab and manually sort the URL, however that’s not all the time possible once they’re lengthy. An alternative choice is to examine the TLS certificates to verify it belongs to the location displayed within the handle bar.
[ad_2]















