[ad_1]
Regardless of having heard the tune in all probability 50 instances within the final two years, I found there are notes in David Bowie’s “Starman” that I’d by no means heard till one morning in early November. That’s after I bought to strive a prototype noise-canceling earbud from xMEMS.
The five-year-old startup focuses on making audio system from microelectromechanical techniques (MEMS) silicon-and-piezoelectric chips. Its current designs are starting to appear in consumer devices, they usually have many benefits over right now’s miniature audio system. These beforehand hidden notes in “Starman” are simply considered one of them. However their peak quantity has by no means been sufficient to beat a technical requirement of noise-cancelling earbuds—20 extra decibels within the bass register. A brand new MEMS tech, known as Cypress, types audible tones by producing and mixing ultrasound and may give chip-scale audio system sufficient oomph for the job and perhaps even lead the tech takeover for different small audio system, like these in automobiles and computer systems.
“Most standard audio system generate sound by actuating and pushing a diaphragm; you’re pushing air to generate sound,” says Mike Householder, vice chairman of selling and enterprise growth at xMEMS. With Cypress, he says, “We’re truly going to make use of ultrasonic modulation and demodulation to create stress and generate sound…that is basically the primary time people are experiencing sound generated differently.”
 The Cypress MEMS speaker chip is about 9 millimeters diagonally.xMEMS
The Cypress MEMS speaker chip is about 9 millimeters diagonally.xMEMS
MEMS chips have already conquered the microphone market, making up nearly all of microphones bought even 5 years in the past, in line with the Yole Group market analysis agency. However audio system demand one thing totally different from MEMS, explains Householder. They should propel a quantity of air, slightly than be pushed by it. xMEMS speakers going into merchandise now are chips with a number of silicon flaps coated in piezoelectric materials that vibrate at audible frequencies.
XMEMS has already delivered a number of benefits of MEMS know-how. MEMS chips specializing in audible frequencies embody very low section distortion. That’s the variation within the timing of an acoustic sign in line with its frequency. In an earlier article, Brian Lucey, a mastering engineer who has labored on 9 Grammy-winning albums, informed IEEE Spectrum:
“Part inaccuracy is so ubiquitous that we merely settle for it…. Driver know-how to date has by no means been capable of be this correct. It’s actually not a query of what does it sound like when it’s inaccurate, as a result of that’s simply regular to our ears. It’s extra a query of what does it sound like when it’s this close to completely correct…. All the things is hitting you on the identical time. There’s no time smear in the best way the sound comes throughout.”
From a producing and engineering standpoint, MEMS is a win, as nicely, argues Householder. For one factor, it’s a much less complicated system, made up of only a single packaged chip and an accompanying IC as an alternative of a posh meeting of coil, magnet, diaphragm, and different components. Coil audio system require labor-intensive manufacturing and testing, partly due to inconsistencies from unit to unit. And MEMS permit for simpler earbud design, as a result of they don’t trigger electromagnetic interference like coil audio system they usually don’t require a selected quantity of air behind the earbud to enhance sound high quality.
MEMS Noise-Cancellation Drawback
All that’s sufficient for some functions, however for “true wi-fi stereo” earbuds there’s a catch. If in case you have a pair, and also you in all probability do, you’ll discover a tiny air vent. It’s there for 3 causes, Householder explains. One is to vent uncomfortable stress from between the bud and your ear canal. One other is to scale back an odd impact the place your personal voice will get amplified inside your head. And the third is to facilitate lively noise cancellation.
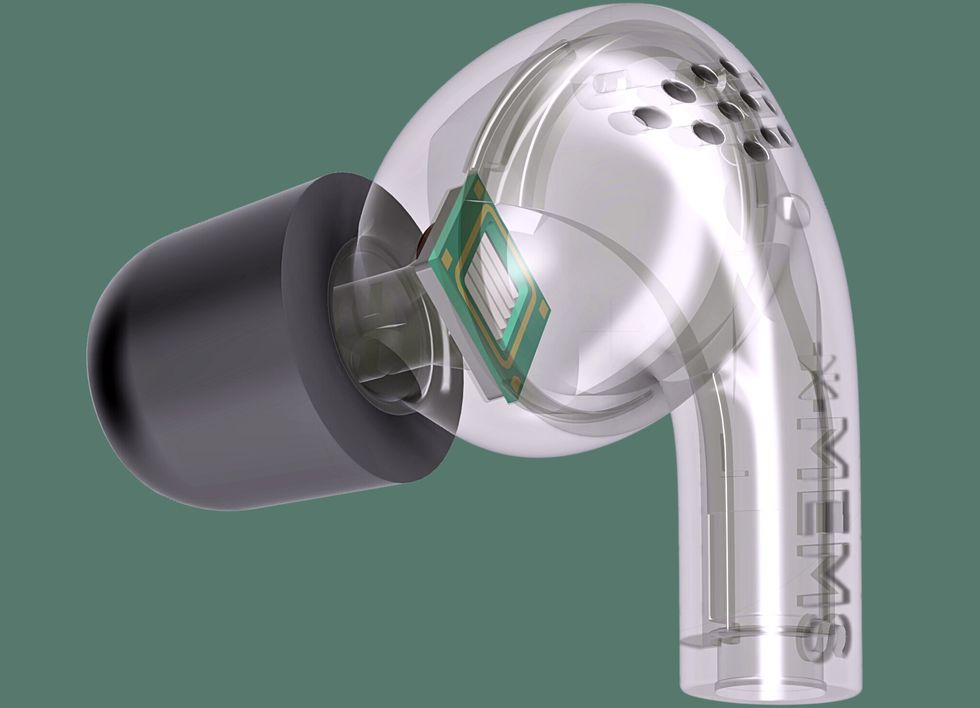 The Cypress MEMS speaker chip is loud sufficient to accommodate lively noise canceling with out a further woofer.xMEMS
The Cypress MEMS speaker chip is loud sufficient to accommodate lively noise canceling with out a further woofer.xMEMS
Energetic noise cancellation depends on algorithms that assume a comparatively steady seal between the bud and your ear. However actual life doesn’t work that manner. The buds shift in peculiar use and the seal shouldn’t be constant. The vent is supposed to be a a lot bigger leak within the system than any small breaks within the seal, overwhelming the small modifications and permitting the noise-cancellation algorithm to do its work, Householder explains.
“The draw back is while you open air to a speaker,” it results low frequencies, he says. “That’s simply the physics of audio system.” In an earbud you’ll usually lose about 20 decibels of low frequency, he says. On their very own xMEMS audio system in units right now can hit 120 dB, and, sure, that’s a fairly unhealthy stage already. However to cancel out the jackhammers and jet engines of the world, you want 140 dB at low frequency.
To make up the distinction with a MEMS system, designers presently pair it with a coil speaker that’s used as a woofer. However xMEMS new ultrasound tech can do the whole job by itself, says Householder.
How xMEMS Ultrasound Tech Works
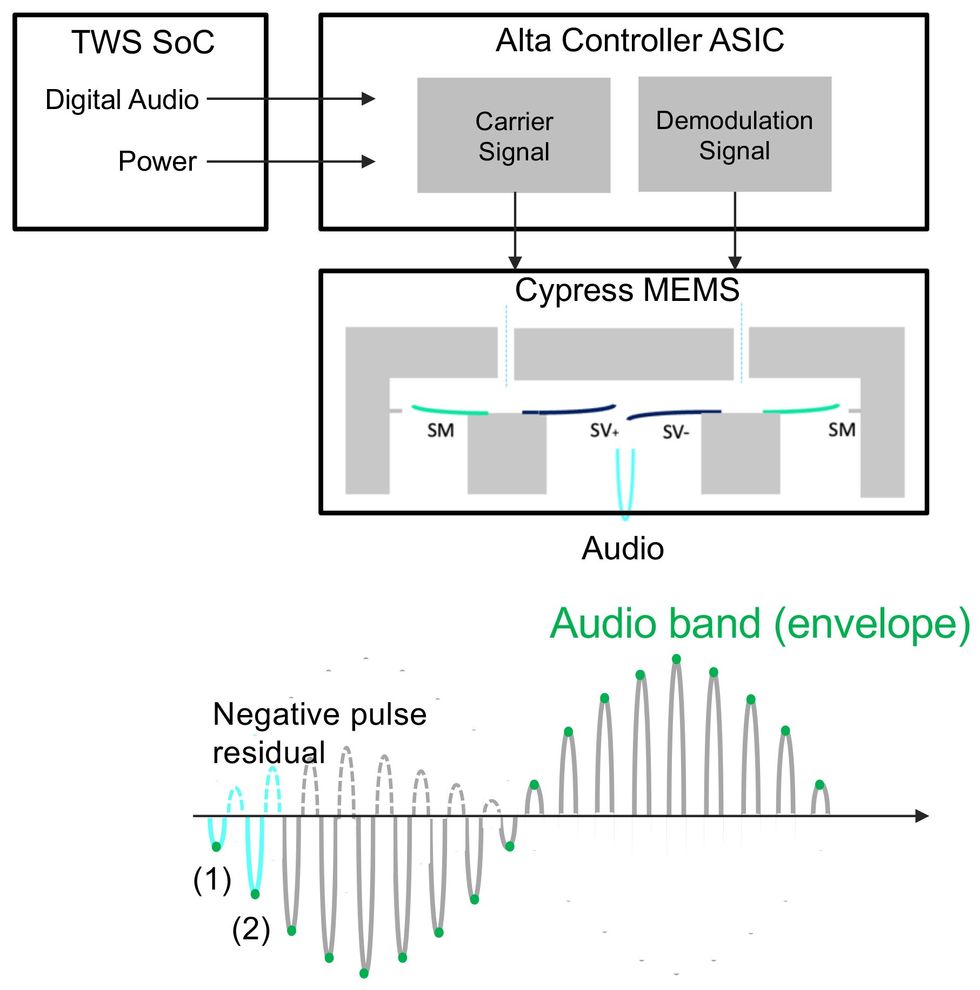 Ultrasound is formed into pulses with an envelope at an audio frequency.xMEMS
Ultrasound is formed into pulses with an envelope at an audio frequency.xMEMS
In step one, a customized IC modulates an ultrasound service sign with the audio sign. The result’s an ultrasound sign whose amplitude is the form of the audio sign. This mixed sign drives a pair of cantilevers that flip the sign into ultrasonic stress waves contained in the speaker chamber. A second sign then periodically vents the chamber, producing a collection of stress spikes whose envelope is the audio sign we hear.
The brand new chip is successfully 40 instances as loud, reaching greater than 140 dB even on the lowest finish of human listening to, 20 hertz. And that’s ok to do the job of lively noise cancellation. Simply as vital, it provides the know-how a path to client merchandise that want much more quantity, resembling smartphones and laptops.
Sure early prospects are already sampling the prototype Cypress chips, and manufacturing samples are set to ship in June 2024, with mass manufacturing set for late 2024.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net
[ad_2]















